- Corneal Surgery

SALK Surgery

- Treatment

- Corneal Surgery
SALK Surgery
Superficial Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (SALK surgery) is a cornea transplant technique where the corneal epithelium and superficial stroma are removed by an eye surgeon. The anterior (front) part of a donor cornea is sutured in its place.
What is SALK - Superficial Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Surgery?
SALK (Superficial Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty) is a corneal transplant surgery used to treat anterior corneal diseases while maintaining the healthy posterior layers of the cornea.
During a SALK surgical procedure a layer of the donor cornea, consisting of approximately one third of the full thickness of the cornea is prepared and is used to replace the anterior part of the patient’s cornea.
This donor tissue is then sutured into place where the tissue has been removed. SALK is a more technically challenging procedure but leaves the eye structurally stronger and there is very little chance of graft rejection. There is also more rapid visual recovery than deeper corneal transplant techniques.
A number of conditions may lead to the cornea losing its transparency and thus visual properties. If these abnormalities are not too deep and situated in the anterior (front) part of the cornea then SALK surgery under anesthesia may be considered an option. These include: Herpes simplex keratitis, contact-lens related infection, scarring and trauma.
Conditions that are particularly amenable to SALK are those characterised by superficial irregular opacities, such as: superficial corneal scarring, Reis-Buckler, granular, and lattice corneal dystrophies. A SALK procedure requires the patient to have a healthy corneal endothelium and posterior stroma.
During a SALK surgical procedure a layer of the donor cornea, consisting of approximately one third of the full thickness of the cornea is prepared and is used to replace the anterior part of the patient’s cornea.
This donor tissue is then sutured into place where the tissue has been removed. SALK is a more technically challenging procedure but leaves the eye structurally stronger and there is very little chance of graft rejection. There is also more rapid visual recovery than deeper corneal transplant techniques.
A number of conditions may lead to the cornea losing its transparency and thus visual properties. If these abnormalities are not too deep and situated in the anterior (front) part of the cornea then SALK surgery under anesthesia may be considered an option. These include: Herpes simplex keratitis, contact-lens related infection, scarring and trauma.
Conditions that are particularly amenable to SALK are those characterised by superficial irregular opacities, such as: superficial corneal scarring, Reis-Buckler, granular, and lattice corneal dystrophies. A SALK procedure requires the patient to have a healthy corneal endothelium and posterior stroma.


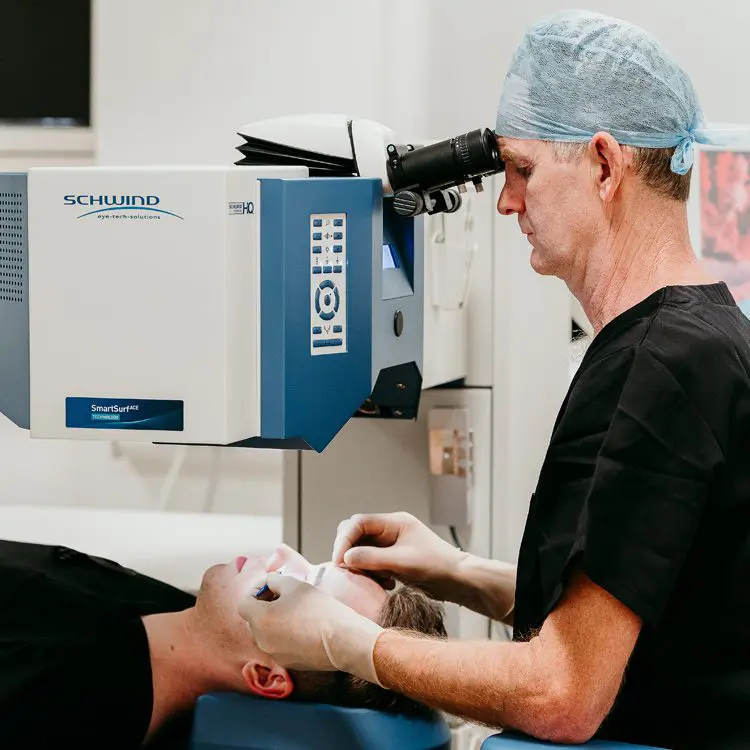
How is Superficial Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty Performed?
- 1.Usually under general anaesthetic in the operating theatre.
- 2.Patient is laid flat on the treatment bed.
- 3.Povidone iodine clean, sterile drape applied, and eyelid support inserted.
- 4.Partial thickness of the central section of the host cornea is removed and donor cornea sutured into place.
- 5.Topical anti-inflammatory and antibiotic drops applied.